Navigating Knee Pain: Indications and Eligibility for Partial Knee Replacement
Introduction
Every diseased or damaged knee joint that requires a surgical intervention need not be totally replaced by artificial prostheses. For partially damaged knee joints, the surgeon resurfaces only one knee joint component with implants, retaining the healthy components of the knee. Similarly, every patient may not be the candidate for partial knee replacement or PKR. The suitability of the procedure depends on the patient's age, bone health, weight, severity of the damage, anatomy and other factors that every surgeon considers before deciding the course of treatment for knee pain.
Partial knee replacement has gained considerable momentum in terms of its increasing use as a knee joint treatment option for treating the affected portion of the knee in the light of its varied clinical benefits to the patients.
The present blog discusses the eligibility, indications, and benefits of partial knee replacement and how to navigate it.
Partial Knee Replacement
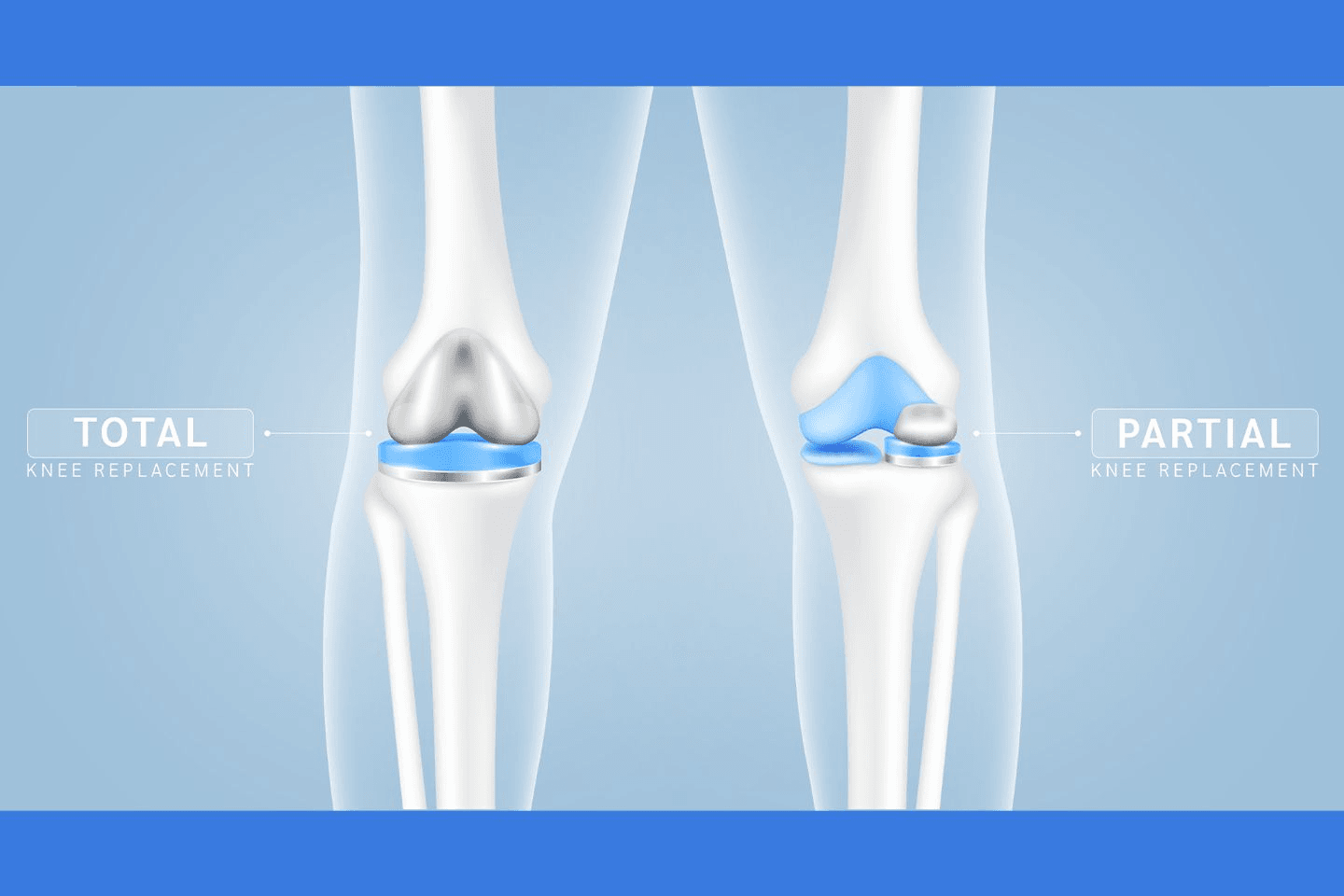
The knee joint comprises three major components: the lateral (outside), medial (inside), and patellofemoral (kneecap) compartments. Partial knee replacement, also known as Unicompartmental Knee Replacement, Unicondylar Knee Replacement (UKA), or Microplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace one of the compartments of the knee joint that is damaged due to arthritis, injury, or any other degenerative condition with an artificial prosthetic device. The treatment is resorted to when all other remedial measures, including physical therapy, medications, and other non-surgical treatment options, do not relieve knee pain, stiffness, restricted range of motion, and associated discomfort.
The anesthesiologist puts the patients either under general or local anesthesia, depending on the clinical need to numb the body. The surgeon resurfaces the damaged part and replaces it with an artificial implant. The removed cartilage is replaced with a plastic spacer that provides a smooth cushion to the knee joint movement. The primary goal of the procedure is to provide relief from knee pain by-
- Resurfacing the damaged part, replacing it with an artificial implant, and
- Keeping the healthy part of the knee intact and restore the natural functionality to the extent clinically possible.
Indications for Partial Knee Replacement
Often, daily life seems challenging, with debilitating pain taking over with every single movement affecting the knee joint in many people. Be it getting up from the bed or chair, going for a stroll outside, climbing stairs, or bending down. The restricted movement due to the associated pain hampers the normal life, affecting the person's quality of life. This calls for a medical diagnosis by a healthcare provider that may include physical examinations, Knee X-rays, or other necessary tests. The common indications of PKR include the following.
- When the diagnosis correlates to specific symptoms isolated to one of the compartments of the knee joint, the healthcare professional may recommend partial knee replacement.
- The most common indication of PKR is joint pain, stiffness, or joint swelling due to arthritis resulting from the wear and tear of the cartilage.
- Injury or history of injury to the knee may also damage one of the parts of the knee joint requiring PKR.
- Osteonecrosis is also considered one of the indications for PKR, where the bone tissues die, causing joint collapse due to the loss of blood supply to the bone.
Eligibility for Partial Knee Replacement
Every knee joint and every person would not be eligible for partial knee replacement surgery. The criteria to qualify for PKR include the following-
- Only one of the joint parts is damaged or affected.
- The patient is under 60 or has a healthy weight (not obese).
- The ligaments of the knee are intact, with good bone health and minimal knee pain while at rest.
- There is no inflammatory disease or knee infection
- No history of surgery requiring cutting of the tibia bone.
- The patient has a good range of knee movement.
- The patient has no knee deformity (bowed or knocked knees).
Advantages of Partial Knee Replacement
Till recently, PKR was less common a treatment option for treating damaged knee joints than total knee replacement. Total knee replacement has been the preferred choice for medical professionals and patients, even in cases of partial damage to the knee joint. However, with time, the many advantages of PKR have contributed to its increasing popularity in recent years, to name a few –
- The procedure is less invasive and, hence, less complex and painful.
- The procedure deals with isolated damaged compartments without dislocating the knee joint.
- It prevents disrupting the tendons and ligaments and, thus, tissue damage, facilitating speedy healing and recovery.
- It restores the natural functionality of the other compartments and the range of motion.
- It enables quicker resumption of routine, with patients able to live an active life within weeks of the treatment.
Post-Surgical Patient Care
The recovery post-PKR depends on the patient's age, health, weight, and activity prior to the procedure as well as post-operative pain management and patient care.
With doctor-prescribed pain-relieving medications and other techniques of ice therapy and knee elevation practice, one can minimize or manage post-operative pain. Scheduled follow-ups with the doctor, wound incision hygiene, professionally guided physical therapy for muscle flexibility and strengthening, a healthy diet, a positive outlook, and consistent efforts are the keys to better healing and quicker recovery.
The Opulent Bionik Gold Knee: The Cutting Edge in Knee Replacement Technology from Meril
The Opulent Bionik Gold Knee is a medical device knee implant that builds on the base science, successes, and learnings gained from the Freedom Knee system. The Opulent Bionik Gold Knee is currently the most biocompatible non-allergic surface material out there, with a mere 0.0008 times ionic release compared to regular Cobalt Chromium products. The system also offers the benefits of an optimized sizing matrix, higher wettability with synovial fluids, low Friction articulation, long-term chemical stability, and superior abrasion resistance for longevity, to name a few.
Conclusion
Partial knee replacement is becoming a preferred choice of patients when treating knee pain. It offers substantial positive surgical outcomes with proper patient selection and correct indications. The surgery provides a feeling of satisfaction to patients as they feel their knees to be natural, even post-surgery. The surgery offers comfort with an improved range of motion and active life after PKR. Like every surgical intervention, this procedure also has its risks and limitations that need to be discussed with the healthcare professional to arrive at an informed decision for knee pain treatment.