Medical Devices
Role of Peripheral Stents in Treating Peripheral Artery Disease
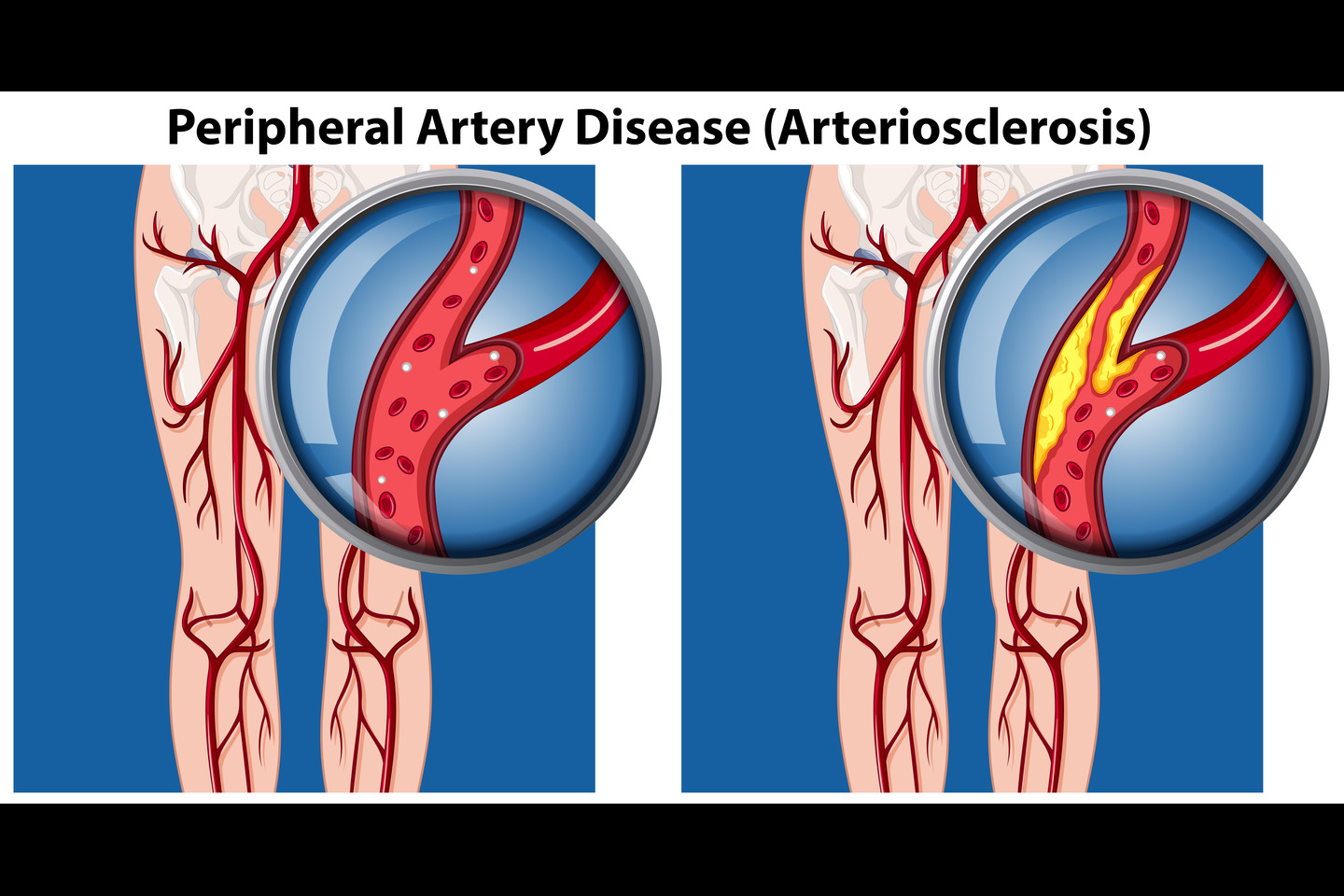
Have you ever felt a sharp pain in your legs while walking or noticed that your feet feel unusually cold? These could be signs of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), a condition that affects many people but often goes unnoticed. If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications. Fortunately, medical advancements have introduced peripheral stents, offering a promising solution for those suffering from this condition. In this article, we will explore what PAD is, how peripheral stents work, and why they are becoming a popular choice for treatment.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Artery Disease is a circulatory condition where narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. This narrowing is primarily due to atherosclerosis, a process where fatty deposits build up on the artery walls, leading to reduced blood flow. PAD commonly affects the legs but can also impact other parts of the body.
Common Symptoms and Complications of Peripheral Artery Disease
The symptoms of PAD vary, but common signs include leg pain while walking (claudication), leg numbness or weakness, coldness in the lower leg or foot, sores on the toes, feet, or legs that will not heal, and a change in the colour of the legs. If left untreated, PAD can lead to severe complications, such as critical limb ischemia, which can result in amputations.
Risk Factors Associated with PAD
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing PAD. These include smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Family history and age also play significant roles, with older adults being more susceptible to the disease.
Traditional Treatments for PAD
Traditionally, PAD treatment begins with lifestyle changes and medications. Lifestyle modifications include quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and adopting a healthy diet to manage weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Medications often prescribed for PAD aim to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. These may include antiplatelet agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and medications to control high blood pressure and diabetes.
Surgical Options for PAD
For more severe cases of PAD, surgical interventions may be necessary. Angioplasty, a procedure that uses a balloon to open up blocked arteries, is commonly used. Sometimes, a stent may be placed during angioplasty to keep the artery open. Bypass surgery, where a graft is used to bypass a blocked artery, is another option for severe PAD cases.
Limitations of Traditional Treatments for PAD
While these treatments can be effective, they are not without limitations. Lifestyle changes and medications require ongoing commitment and may not be sufficient for advanced PAD. Surgical options, while effective, come with risks such as infections and long recovery times. This is where peripheral stents offer a promising alternative.
Introduction to Peripheral Stents
Peripheral stents are small, metal mesh tubes inserted into an artery to keep it open and allow for better blood flow. They are specifically designed to treat peripheral arteries, particularly in the legs. The primary purpose of peripheral stents is to provide a minimally invasive solution to keep the arteries open and improve blood flow, thereby alleviating PAD symptoms.
How Stents Work to Alleviate PAD Symptoms
During the procedure, a stent is placed within the affected artery using a catheter. Once in place, the stent expands, pressing against the artery walls and keeping them open. This process helps restore proper blood flow to the affected limb, reducing pain and improving mobility.
Types of Stents Used in Peripheral Arteries
There are different types of peripheral stents, including bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents. Bare-metal stents are simple metal mesh structures while drug-eluting stents are coated with medication that helps prevent the artery from becoming blocked again. The choice of stent depends on the patient's specific condition and the healthcare provider's recommendation.
Advantages of Peripheral Stents for PAD Patients
Minimally Invasive Treatment: One of the significant benefits of peripheral stents is that they offer a minimally invasive treatment option. Unlike bypass surgery, which requires large incisions and lengthy recovery times, stent placement is done through small incisions, often under local anesthesia. This results in shorter hospital stays and faster recovery.
Improved Blood Flow and Symptom Relief: Peripheral stents effectively improve blood flow in the affected arteries, which leads to significant relief from PAD symptoms. Patients often experience reduced pain, better mobility, and an overall improvement in their quality of life.
Long-term Efficacy: Peripheral stents have shown to provide long-term efficacy in keeping arteries open. Drug-eluting stents, in particular, offer added benefits by releasing medication that helps prevent restenosis, which is the re-narrowing of the artery.
Enhanced Quality of Life: The combination of minimally invasive treatment, improved blood flow, and long-term efficacy contributes to a significantly enhanced quality of life for patients. They can return to their daily activities more quickly and with less pain, which is a substantial improvement over traditional surgical options.
Patient Eligibility and Considerations for Peripheral Artery Disease
Not all patients with PAD are candidates for peripheral stents. The decision depends on several factors, including the location and severity of the artery blockage, the patient's overall health, and their ability to undergo the procedure. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best treatment plan.
Promesa by Meril
Promesa by Meril is a stent designed for the treatment of peripheral artery disease. This high-durable stent has a hybrid cell design that offers a balance of flexibility, conformability and kink resistance. Built with a nickel-titanium alloy, this stent reduced microcracks and the possibility of a stent fracture in the future.
Final Thoughts
Peripheral stents represent a significant advancement in the treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease. They offer a minimally invasive, effective solution that can improve blood flow, relieve symptoms, and enhance the quality of life for many patients. While traditional treatments still play an essential role, peripheral stents provide a valuable option for those seeking an alternative. As with any medical treatment, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual circumstances.
Reference Links:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350557
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-artery-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350563
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17357-peripheral-artery-disease-pad
https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/discharge-instructions/angioplasty-and-stent-placement-peripheral-arteries-discharge#:~:text=A%20stent%20is%20a%20small,help%20keep%20the%20artery%20open.
https://www.upmc.com/services/heart-vascular/tests-procedures/peripheral-angioplasty-stenting#:~:text=Angioplasty%20and%20Stenting-,Peripheral%20Angioplasty%20and%20Stenting,open%20and%20improve%20blood%20flow.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3377569/#:~:text=A%20stent%20is%20a%20wire%20mesh%20%E2%80%9Cscaffold%E2%80%9D%20that%20is%20implanted,are%20available%20in%20varying%20length.
https://www.medstarhealth.org/services/peripheral-angioplasty-and-stenting
https://www.theheartcarecenter.com/contents/procedures/stents/peripheral-stent





