What is an Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD)?
An Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD) is a small, plastic, copper or hormone containing device, which is placed inside the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It comes in different types, sizes and shapes to suite different women. Depending upon your choice of contraception period, it can be inserted for 3-5-10 years.
What are the different types of IUCDs ?
IUCDs are broadly classified as:
1. Copper IUDs - containing copper.
2. Hormonal IUDs - containing Levonorgestrel.
Action & Efficacy of Intrauterine Contraceptive Device
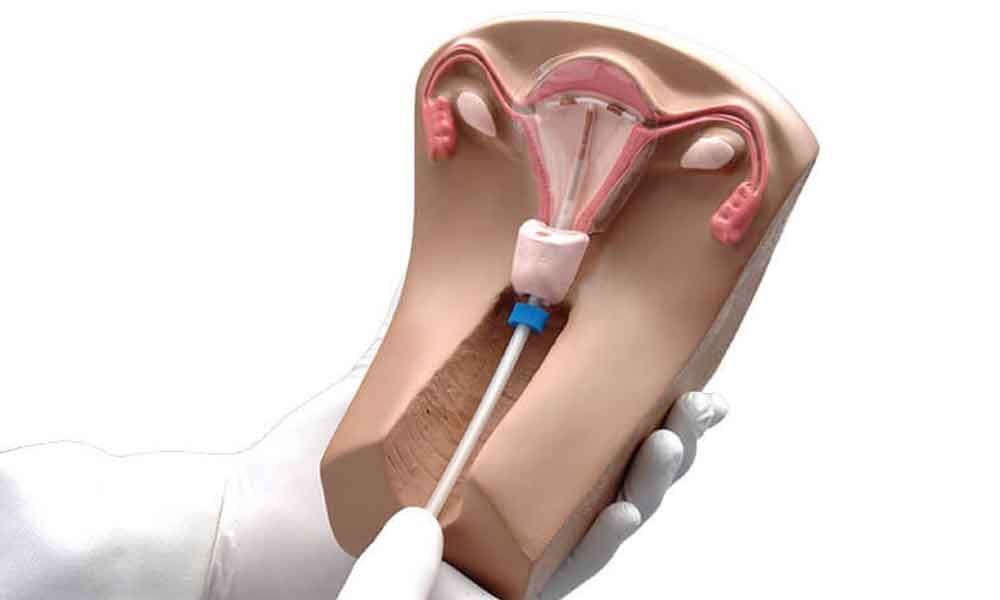
How is an IUCD inserted?
The doctor or nurse will examine you internally to check the position and size of the uterus before they put in an IUCD. Sometimes, they will check for any possibility of an existing infection. This can be done before or at the time of inserting an Intra Uterine device( IUCD).
You may also be given antibiotics at the same time during IUCD insertion. Fitting an IUCD takes about 10-15 minutes. Once an IUCD is inserted it could be uncomfortable or painful for some women, and you might want to use a local anesthetic. It may cause some side effects like Head ache and Nausea which usually settles after the first few months of usage. Your doctor or nurse should talk to you about this beforehand.
You may experience a period-type pain and light bleeding for a few days after the IUCD is inserted. Pain relieving drugs can help to reduce the pain.
source:CathedralMedical
How does an IUCD work?
Primarily works by disrupting sperm mobility and damaging sperm, an Intra Uterine Contraceptive Device prevents pregnancy by making it difficult for the sperms to survive inside the uterus or to reach the egg in the fallopian tube. It may also work by stopping a fertilized egg from getting implanted inside the uterus. However it does not cause an abortion.
An Intra Uterine Contraceptive device also acts as a spermicide within the uterus, increasing levels of copper ions, prostaglandins, and white blood cells within the uterine and tubal fluids. Increased ions inhibits sperm’s mobility and viability, preventing sperm from traveling through the cervical mucus.
In an Intra Uterine Contraceptive device, the horizontal arms of T exerts mechanical forces on the uterine cavity and also take the shape of the uterine cavity
Usage & Benefits of an Intrauterine Contraceptive Device
When can an IUCD be removed?
A trained doctor or a nurse can take Intra Uterine Contraceptive Device out at any time by pulling gently on the thread tied at the end for removal. Sperms can live for up to seven days inside your body and could cause a pregnancy once the IUCD is removed.
If you are not going to have another IUCD inserted, and you do not want to become pregnant, use additional contraception, such as condoms, for seven days before the IUCD is taken out. This is to stop sperms getting into your uterus.
Your fertility returns to normal as soon as the IUCD is taken out.
What are the advantages of an IUCD?
More than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy
Cost effective method
Easy to use
Safe to use while breast feeding
Long intrauterine life (5 -10 Years)
IUCD insertion involves no touch technique is employed while insertion
IUCD insertion doesnot interrupt with foreplay or intercourse.
In the use of Hormonal Intra uterine device, reduces heavy menstrual bleeding and reduces the risk of Ectopic Pregnancy.
Can be removed whenever you have problems or want to stop using it. Fertility returns with the first ovulation cycle following the IUCD removal
Can be inserted after a normal vaginal delivery, a cesarean section, or a first trimester abortion
IUCD insertion is safe after abortion or miscarriage with no infection.
IUCD insertion is safe for all women including adolescents and women over 40
IUCD insertion may effectively relieve endometriosis and is less likely to cause side effects than high-dose progestin.
IUCD insertion does not cause weight gain
What are the limitations of an IUCD?
You need an internal examination to check whether IUCD is suitable so that it can be inserted.
Only a health professional can insert/remove the IUCD
Your periods may be heavier and longer with Copper IUD insertion.
Does not protect against HIV or any other STDs.
Could be spontaneously expelled out of the uterus, due to various factors.
Insertion of an IUD may precipitate a seizure in women suffering from epilepsy. Special care is therefore recommended during insertion
TIME OF IMPLANTATION OF AN IUCD(Intrauterine Contraceptive Device)
After childbirth –(Insertion of an IUCD)
4 to 6 weeks after birth After accidental or induced abortion
Shortly following the first trimester of abortion (aseptic).
After the second trimester of abortion, it is best to wait until the involution of the uterus is complete.
Directly after delivery of the placenta (post-placental insertion)
Cycle of Menstruation – ( Insertion of an IUCD)
It can be inserted during any point during the menstrual period if it is reasonably evident that the woman is not pregnant and has not had intercourse without contraceptives.
Insert after menstruation offers the following advantages:
1) Breastfeeding is omitted
2) The penetration is smoother due to the widening of the cervical canal
3) Any mild bleeding caused by injection is less likely to upset the customer.
CONTRAINDICATIONS OF AN IUCD
ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATIONS OF AN IUCD
Malignant Disease of the genital tract
Vaginal bleeding
Pregnancy
Past history of ectopic pregnancy or predisposing factors
Genital tract infections
Sexually Transmitted disease during last 12 months
History of abortion with infections during last 3 months
Uterine malformations
Allergy to Copper

RELATIVE CONTRAINDICATIONS OF AN IUCD
Anaemia
Vulvular heart disease
Coagulation Disorders
Anti-inflammatory treatment
Wilson's Disease
Multiple exposure to different sexual partners PR
What precautions should be taken before insertion of Intrauterine Contraceptive Device?
Prior to insertion, physical examination should be done which including a pelvic examination, cervical smear, and if possible, appropriate tests for diagnosing sexually transmitted diseases.
After insertion IUCD users should be re-examined shortly after the first period and after immediate post-abortion or post-partum insertion monthly during the first three months. Thereafter, appropriate examination should be carried out at regular intervals i.e every six months.
If IUCD threads cannot be felt in a woman who has not noticed expulsion, examination is necessary to exclude perforation or unnoticed expulsion. Ultrasound or X-ray may be used to locate the device.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) - The risk of developing PID in women using an IUD is only increased in the first 20 days after insertion; thereafter the risk of PID is similar to the risk in women without an IUD. The occurrence of PID may also be due to other factors, such as contraction of a sexually transmitted disease. In mild cases the diagnosis should be established and treatment with antibiotics started. If there is no response after 24 hours the IUD should be removed. In moderate cases with more definite clinical signs the IUD should be removed before starting antibiotic therapy and the patient referred for a gynecological opinion. In severe cases associated with marked lower abdominal pain and fever the IUD should be removed and the patient should be admitted to hospital.
Medical Reasons for Removal of IUCD (Intrauterine Contraceptive Device)
Pregnancy PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
Excessive and persistent bleeding or cramping.
Perforation of the cervical or uterine wall. This is extremely rare with Meri Te but if it should happen, the device should be removed
Downward displacement of Meri Te into the cervical canal
Translocation
Additional Warnings during removal of Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD.)
IUCDs do not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) or any other sexually transmitted disease
Insertion of an IUD may precipitate a seizure in women suffering from epilepsy. Special care is therefore recommended during insertion.
