Medical Devices
Handheld Robotic surgery v/s traditional laparoscopic surgery
Introduction
Surgical interventions have undergone drastic advancements in the approach, usage of instruments, the role of human intervention, the degree of freedom in operating these instruments, and the introduction of new, innovative, more articulated, and dexterous surgical instruments for the surgeons on the table. Each with a solution-driven approach, these advancements cater to the ever-changing clinical needs of healthcare. The ultimate goal of every surgery is successful surgical and patient outcomes and care; surgeons and healthcare providers constantly strive to leverage their experience and knowledge for higher efficiency, accuracy, and precision on the operating table, using the various tools at their disposal.
The advent of laparoscopic surgery arose from the need to overcome the challenges of traditional surgery and the subsequent introduction of robot-assisted surgery aimed to meet the limitations of laparoscopic surgeries. The robot-assisted console-driven surgical mechanism is replaced by handheld surgical devices, which have the added advantages of more articulated instruments with dexterous handling and better precision.
The blog discusses traditional laparoscopic and handheld robotic system and how they are different in terms of their surgical approach, operation, performance, and outcomes.
Laparoscopic surgery- the need and benefits
Traditional surgeries, though the standard of care for years with their larger incisions and more tissue scarring, leading to chances of incision site infection, slow healing, and longer recovery time, required an alternative. Laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive approach, was introduced, causing less pain and scar damage, faster healing and recovery, shorter hospitalization, and better post-operative patient care and management.
Laparoscopic surgeries are minimally invasive procedures for the abdominal, pelvis and thoracic regions. With smaller incisions, the procedure uses a laparoscope camera to view the patient's inside organs and laparoscopic instruments like the hook, spatula, scissors, needle driver, trocars, and bowel grasper.
These procedures are manually operated or robot-assisted. In the case of manual operations, the surgeon uses traditional laparoscopic instruments through smaller incisions for surgical procedures.
In the case of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon performs and guides the robot from the nearby console without being next to the patient, using three-dimensional images to access the patient's anatomy.
Need for Robot-Assisted Surgery
The traditional laparoscopic instruments are larger, long, and straight, with rigidly attached jaws to the tips. These features of the instruments make it challenging for the surgeons to operate and handle the movement of the instruments when inserted through smaller incisions on the patient's body. The surgeons experience physical and mental discomfort due to prolonged posture while operating through small access areas, affecting their surgical efficiency and accuracy. With limited freedom and lack of articulation, the surgeons find it challenging to reach out to the surgical site and touch and feel the tissues, thus losing the cognitive understanding of tissue characterization (identifying the healthy and unhealthy tissues during surgery).
Robotic laparoscopic surgery provides the much-needed solution for precision, accuracy, and efficiency during surgery by ensuring that the surgeons need not hold and maneuver the instruments standing next to the patient but can control the surgical operations from a nearby console using a high-definition, three-dimensional camera.
Though robot-assisted console-driven workflow setup provided the desired solution of less human intervention with a high degree of physical and mental comfort, it came with certain limitations. These limitations include the surgeon's lack of proximity to the surgical site, mobility, and easy accessibility due to the large scale and size of the assisted platform. The workflow set, its associated high installation and maintenance costs, and management posed further challenges to the operational success of the system.
Handheld surgical devices are the smart surgical devices that have come into the market to bridge the gap between traditional and robot-assisted laparoscopic instruments. These handheld devices come as an affordable alternative, ensuring less capital investment while providing the required dexterity, freedom of motion, and articulation, promising effective surgical maneuvering.
Difference Between Traditional Laparoscopic Surgery and Handheld Robotic Surgery
Both procedures follow the same approach of minimal invasiveness through smaller incisions in the abdomen. However, they are different in terms of the technology used in the surgeries.
- Traditional laparoscopic surgery uses a two-dimensional camera, while robot-assisted handheld surgery uses a three-dimensional camera view.
- In the case of traditional laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon uses excessive arm movements to access and operate at the surgical site since it doesn’t have any additional degrees of freedom to articulate the end effector tip of the instrument.In handheld devices, the surgeon uses the handheld system (driven by software) to reach to the target anatomy with an articulated tip to treat the defect.
- Traditional procedures use straight, and more rigid laparoscopic instruments, making it challenging for surgeons to gain proximity to the surgical site and maneuver the instruments effectively.The handheld surgical devices are motorized and software-driven, enhancing the surgeon's efficiency, competence, and accuracy in handling complex surgeries.
- In traditional laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon experiences mental and physical discomfort due to challenges in accessing the inside of the patient's body through small access points and prolonged posture while handling rigid instruments with a limited range of motion, often affecting their performance and efficiency.Handheld devices rule out these challenges by facilitating ease and efficacy to the surgeons on the operation table through tailored design and optimal fitting devices, efficient articulation, agility and dexterity, ease in handling, and ergonomic flexibility.
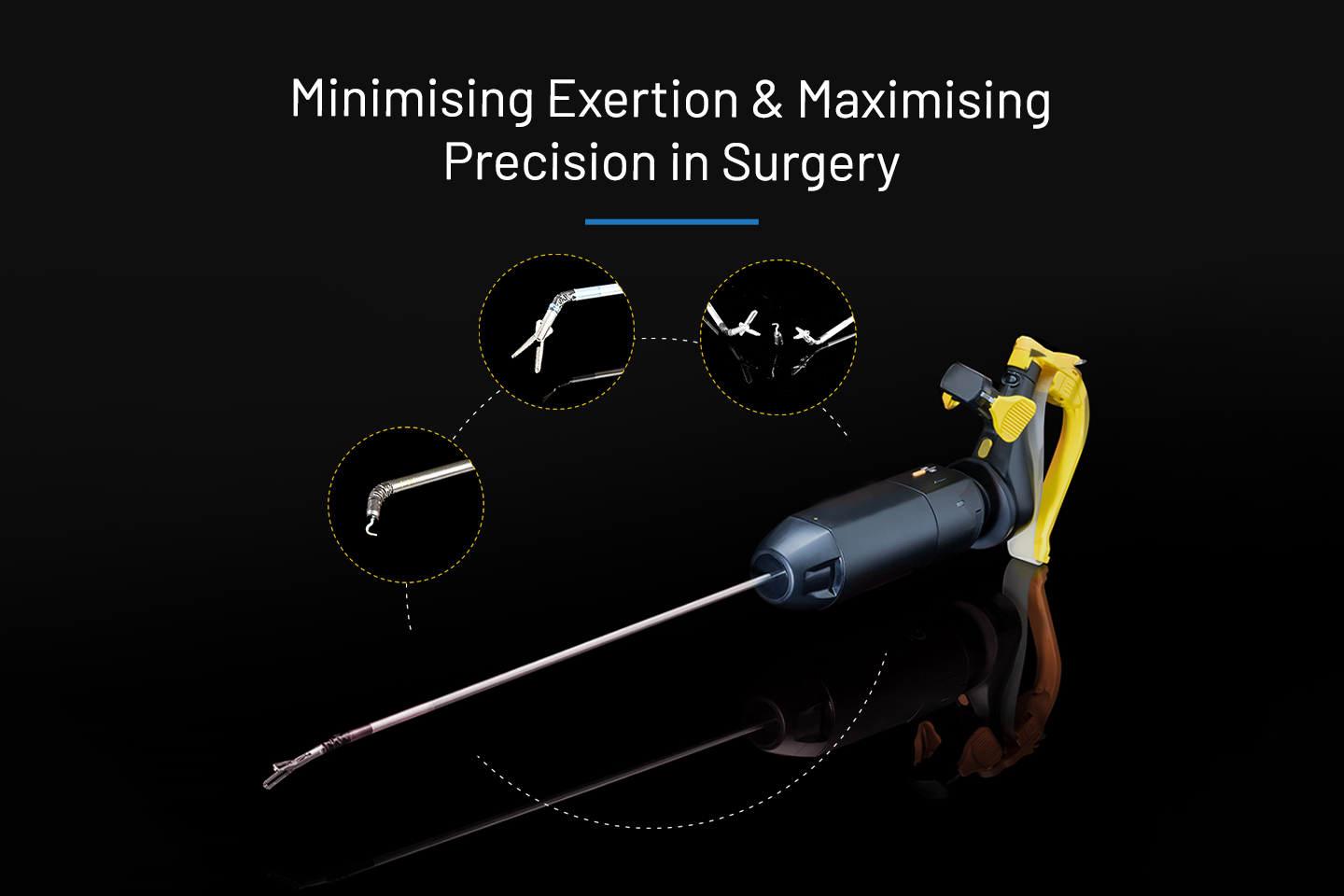
HANDX® by Meril
HANDX® by Meril is a handheld solution for surgeons that combines the advantages of robotics with the benefits of handheld instruments. FDA-cleared and CE-marked (MDA), HANDX® is a robust yet compact and lightweight and portable system that is easy to use and proves to be a powerful tool for surgeons in MIS practice.
It is a simplified, modular, and cost-effective platform ensuring suitability for hospital setup, no workflow disruption and maintenance, as a flexible economic model. The device facilitates complex MIS maneuvering, allowing efficient articulation and smooth access to technically challenging areas. HANDX® is suitable for varied surgical approaches. The device comes with various working instrument tips.
Conclusion
The field of minimally invasive surgeries has evolved from traditional laparoscopic surgeries to the present-day handheld smart devices that facilitate effective maneuvering of surgical operations. With robot assistance, smart handheld devices aim to bring the best laparoscopic approach to surgery to enhance the surgeon's capabilities and efficiency while performing the most complex surgeries. Handheld devices are taking the driver's seat in navigating the future of laparoscopic surgeries toward optimal surgical efficiency and positive patient care and outcomes.
Disclaimer
This promotional material is illustrative of HANDX - Handheld Robotic System and intended for information purposes only and may not be comprehensive for product usage. All the illustrations in the blog are artistic representations; the actual product may vary and shall not be considered as engineering drawings or photographs to scale. The actual procedure performed under the standard operative environment by a medical professional may be different and not similar to the demonstrations portrayed herein. Medical professionals are advised to read user manuals before use and contact the company representative for more information and guidance on the Product. All intellectual property rights related to the HANDX device and the content of this promotional material are the sole property of HUMAN XTENSIONS or its licensors. Any unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of the content is strictly prohibited. Reference to the product in this brochure does not imply that it is registered or available in your country. Meril represents HANDX in assigned territory only.
References
https://www.medstarhealth.org/blog/how-does-robotic-surgery-differ-from-laparoscopic-surgery
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S240584402203849X
Handheld Robotics in Laparoscopic Surgery | Meril Life





